- Visibility 268 Views
- Downloads 18 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.jdpo.2021.068
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Lip Lumps Need not be mucocele
- Author Details:
-
P.S. Muthu Subramanian *
-
P Jayaganesh
Introduction
Lip lumps can present to both the general practitioner and to ENT department. Oral mucoceles is the most common benign soft tissue masses of minor salivary glands.[1] Tumors of the minor salivary glands occur most commonly on palate, buccal mucosa, and tongue. Occurrence on the lips appears to account for approximately 5% for these tumors, with most occurring on the upper lip.[2] We here report three lip lump cases which were clinically suspected to be a mucocoele turned out to be an unexpected diagnosis which only became clear following excision and histological examination.
Patient 1
A 23 year old female came with complaints of swelling in his upper lip for 2 years. There was no history of pain, trauma, fever and no history of discharge from the swelling. Excision biopsy was done and specimen was sent for histopathological examination.
Histopathological examination showed mucinous salivary glands admixed with well circumscribed benign neoplasm epithelial elements arranged in sheets, cords and ducts with scant eosinophilic cytoplasm surrounded by a chondromyxoid stroma. ([Figure 1])
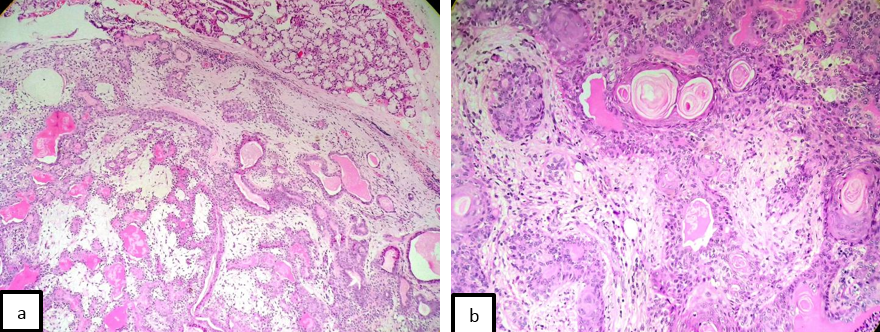
Patient 2
A 57 year old female presented with a swelling in the left side upper lip for past 3 months which was 3x 3 cm gradually increasing in size. Biopsy was done and sent for histopathology.
Histopathological examination revealed a neoplasm composed of infiltrating sheets, cords, focal cribriform patterns of cells with scant cytoplasm and hyperchromatic angulated nuclei. The margins of the lesion are infiltrated by the tumor ([Figure 2]).
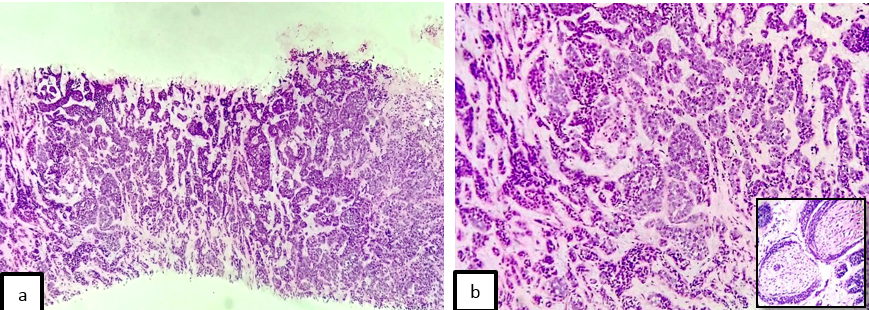
Patient 3
A 23 year old male came with complaints of swelling in his lower lip for 3 years which was increased in size since 2 months. No H/O pain, fever / discharge. Excision biopsy was done and sent for histopathology.
Histopathology showed stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium with underlying subepithelium showed bundles of hypertrophic nerve fibres which suggested a neuroma ([Figure 3]).

Discussion
Salivary gland tumors are rare, constituting 2– 6.5% of all head and neck tumors.[3] Tumors of the minor salivary gland account for 22% of all salivary gland neoplasms. According to Patil., etal Mucocele which is the second most common lesion in lip next to infectious etiology is seen in 29.8%.[4]
Pleomorphic adenoma or mixed tumor is a benign tumor of major salivary gland. It usually present as painless, slow-growing swelling of long duration.[5], [6] The palate is considered as the most common intraoral site (42.8–68.8%), followed by the upper lip (10.1%) and cheek (5.5%). Other rare sites include the throat (2.5%), retromolar region (0.7%), floor of the mouth and the alveolar mucosa.[7] Histopathologically, pleomorphic adenoma is composed of epithelial and myoepithelial elements arranged in a variety of patterns embedded in the mucopolysaccharide stroma. The tumor has a false capsule which is formed as a result of fibrosis of surrounding salivary parenchyma due to compression of the tumor.[8]
ACC is a malignant salivary gland neoplasm which was first described by Robin and Laboulbene in 1853.Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) is a rare malignant slow growing neoplasm of the salivary glands with poor prognosis.[6] It is the most common malignant neoplasm that occurs in minor salivary gland.[9] Intraorally, the palate is the most common site, comprising ~50% of all malignant palatal tumours.[10] Less common sites of involvement include the lower lip, retromolar-tonsillar pillar region, sublingual gland, buccal mucosa, and floor of the mouth.[11] In a study Waldron et al[12] reported 426 cases of intraoral minor salivary gland neoplasms, and identified two cases of ACC on the upper lip. Histologically, this neoplasm is composed of duct-lining epithelial cells and myoepithelial cells, arranged in cribriform, tubular or in solid patterns. Contiguous perineural invasion is a hallmark of ACC.
Traumatic neuroma is a non-neoplastic proliferation of a nerve occurring in response to an injury or surgery. As oral mucosa has rich nerve supply, lies close to the connective tissue and minor salivary glands, any surgical trauma to hard or soft tissue leads to cutting of nerve fascicles. If the nerve ends not reestablished , Schwann cells proliferate and formation of neural elements resulting in neuroma Clinically, it presents as a firm nodule that is occasionally tender or painful on palpation, Microscopically, the cells are arranged in short fascicles, whorls, or even in a storiform pattern.[13]
Conclusion
Pleomorphic adenoma and adenocystic carcinoma of lips were unusual neoplasm presenting in the lip as a lump mimicking a mucocele. As these were rare in this location, without proper clinical examination and histopathological examination, the neoplasm may go unnoticed as practitioners should note that these tumors may recur after the surgical excision. Adjuvant radiotherapy should be given post surgery in cases showing microscopic evidence of tumor in excision margins or if perineural invasion is noticed to achieve better control of disease. Proper clinical history regarding surgery or trauma to be asked.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this paper.
Source of Funding
None.
References
- C B More, K Bhavsar, S Varma, M Tailor. Oral mucocele: a clinical and histopathological study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol: JOMFP 2014. [Google Scholar]
- G P Bhandarkar, K V Shetty. Differential diagnoses of elevated lesions of the upper lip: an overview. J Cancer Res Ther 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A K El-Naggar, J K Chan, J R Grandis, T Takata, P J Slootweg. WHO classification of head and neck tumours. International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- S Patil, S Maheshwari. Prevalence of lip lesions in an Indian population. J Clin Exp Dent 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J A Regezi, J Sciubba, R C Jordan. Oral pathology: clinical pathologic correlations. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- S P Kataria, P Tanwar, D Sethi, M Garg. Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Upper Lip. J cutan Aesth Surg 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- T Dalati, M R Hussein. Juvenile pleomorphic adenoma of the cheek: a case report and review of literature. Diagn Pathol 2009. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- B T Varghese, P Sebastian, E K Abraham, A Mathews. Pleomorphic adenoma of minor salivary gland in the parapharyngeal space. World J Surg Oncol 2003. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- K Bjørndal, A Krogdahl, M H Therkildsen, J Overgaard, J Johansen, C A Kristensen. Salivary gland carcinoma in Denmark 1990-2005: a national study of incidence, site and histology. Results of the Danish Head and Neck Cancer Group (DAHANCA). Oral Oncol 2011. [Google Scholar]
- M R Darling, J W Schneider, V M Phillips. Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma: a review and comparison of immunohistochemical markers. Oral Oncol 2002. [Google Scholar]
- B Bianchi, C Copelli, R Cocchi, S Ferrari, N Pederneschi, E Sesenna. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of intraoral minor salivary glands. Oral Oncol 2008. [Google Scholar]
- W Ca, M Sk, D R Gnepp. Tumors of the intraoral minor salivary glands: a demographic and histologic study of 426 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1988. [Google Scholar]
- A Triantafyllou, P Coulter. Structural organization of subgemmal neurogenous plaques in the foliate papillae of tongue. Hum Pathol 2004. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Subramanian PM, Jayaganesh P. Lip Lumps Need not be mucocele [Internet]. IP J Diagn Pathol Oncol. 2025 [cited 2025 Sep 04];6(4):319-321. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jdpo.2021.068
APA
Subramanian, P. M., Jayaganesh, P. (2025). Lip Lumps Need not be mucocele. IP J Diagn Pathol Oncol, 6(4), 319-321. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jdpo.2021.068
MLA
Subramanian, P.S. Muthu, Jayaganesh, P. "Lip Lumps Need not be mucocele." IP J Diagn Pathol Oncol, vol. 6, no. 4, 2025, pp. 319-321. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jdpo.2021.068
Chicago
Subramanian, P. M., Jayaganesh, P.. "Lip Lumps Need not be mucocele." IP J Diagn Pathol Oncol 6, no. 4 (2025): 319-321. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.jdpo.2021.068
