Introduction
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) accounts for 80% of thyroid carcinomas with a 10 year survival over 90%, whereas, anaplastic carcinoma (AC) is an aggressive variant which represents 0.2-2% of thyroid carcinoma and carries worst prognosis.1, 2, 3, 4 Although it may occur de-novo, in 40% cases it culminates from transformation of a terminally differentiated thyroid carcinoma as a synchronous or metachronous involvement; PTC being the commonest pre-transformational subtype.1, 2, 3, 4 Majority of the cases reported till date showed this transformation within the thyroid or at metastatic sites in known cases of PTC who had developed anaplastic transformation (AT) years after diagnosis of PTC.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21
Metastatic AT poses a diagnostic challenge especially when primary site shows no such transformation. Occult primary further adds to the dilemma. Our case is unique as it presented with AT in metastatic site with hidden/occult primary, hence posed a diagnostic challenge even after IHC. Hence, we report this unusual case to emphasize the fact that rapid dedifferentiation of PTC to AT can occur even when primary focus is hidden.
C ase Presentation
An elderly lady aged 75 years, presented with rapidly enlarging, right sided painless neck mass since one month. Her routine blood counts were within normal limits and thyroid function tests showed euthyroid status. USG suggested colloid goitre with foci of calcification and a mass in the right side of neck separate from thyroid. CT scan showed space occupying lesion with calcifications, in the right side of neck likely to be of neurogenic origin with right cervical and supraclavicular lymph nodes. Tru cut needle biopsy of the neck mass was done which showed fibromuscular tissue with an infiltrative tumor showing squamoid morphology. The tumor was composed of clusters of polygonal cells having hyperchromatic nuclei and eosinophilic to clear cytoplasm (Figure 1). Preliminary biopsy diagnosis was metastatic poorly differentiated carcinoma possibly a squamous cell carcinoma. IHC was done for histologic typing and site of origin. Keeping in mind, the most likely possibility of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma, the primary panel included CK, CK7, CK20 & p63. The tumour cells expressed CK, CK7, p63 while CK20 was negative (Figure 2). But as CK7 was expressed (squamous cell carcinomas are negative for CK7 and CK20), we added PAX8, TTF1, GCDFP and CA125 in the secondary panel (Figure 3). Strong nuclear expression of TTF1 and PAX8 confirmed thyroid as the primary offender and ruled out lung carcinoma. Both GCDFP and Ca 125 were negative. However, expression of p63 along with CK7, PAX8 and TTF1 suggested possibility of either some variant of PTC, AC or poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma. But, in spite of intentional search no nuclear features of PTC could be seen. With this histodiagnosis, the patient was subjected to total thyroidectomy along with excision of right neck mass and lymph nodes. The thyroidectomy specimen measured 7x4x2cm. Cut surface showed two tiny grey white nodules measuring 0.5 cm and 0.3 cm in diameter in right lobe and 1.0 cm nodule in the left lobe. Rest of the thyroid showed brown gelatinous appearance with speckled tiny grey white areas. The right side neck mass along with lymph nodes measured 4.5x2.5x1 cm. Cut surface showed grey white appearance (Figure 4). Microscopic examination of thyroid showed multinodular goiter displaying degenerative changes along with multiple foci of tumor composed of round to oval cells having optically clear nuclei with crowding, overlapping and nuclear grooves arranged predominantly in follicular pattern and focally in branching papillary pattern (Figure 5). Fibrovascular cores of the papillae showed lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
The soft tissue mass and lymph nodes showed a metastatic tumor composed of nests and sheets of round to polygonal cells having pleomorphic, pale, vesicular nuclei and eosinophilc cytoplasm showing squamoid differentiation and focal cytoplasmic clearing. Few areas showed sarcomatoid morphology with spindle cells having pleomorphic nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm arranged in interlacing fascicles and bundles. Transition from carcinomatous to sarcomatous area was also evident. Interspersed multinucleated tumor giant cells, increased mitoses and vascular tumor emboli were seen (Figure 6). Paucicellular areas showed keloid like hyalinization, extensive fibrosis and sclerosis. One of the lymph nodes showed squamoid areas and numerous psammoma bodies (Figure 7). We rendered a final diagnosis of Multifocal Papillary thyroid carcinoma with anaplastic transformation in the metastatic lymph node and soft tissue of neck.
Table 1
Anaplastic transformation of thyroid carcinoma at distant sites.
|
Author/ year |
Age/sex |
Site of metastasis |
Period/ Course of disease |
|
Sotome K et al 2007 4 |
82/F |
Retroperitoneum, bones |
17yrs |
|
Takeshita Y et al 20087 |
81/F |
Liver |
|
|
Ito Y et al 20086 |
64/M 80/F 51/F 79/M |
Cervical nodes, lungs 3 yrs Simultaneous-Cervical nodes, lung Submandibular, axilla, cervical nodes Cervical nodes, lungs |
Died - 5mths Alive 7yrs Died-10mths Died 3mths post-op. |
|
Al Qsaus W and Miller ID 20095 |
83/M |
Lung |
10yrs |
|
Kaushal S et al 201112 |
52/f |
Shoulder |
8 yrs. |
|
Nakayama R et al 201210 |
55/F |
Pelvis |
|
|
Abe T et al 201411 |
61/M |
Lungs with malignant pleural effusion. |
|
|
Solomon JP et al 20152 |
64/M |
Cervical node, axilla and retroperitoneum |
25yrs expired |
|
Benedict M and Costa J 2016 18 |
53/F |
Lungs with pleura, aorta, pericardium, adrenal, mediastinal, hilar and abdominal lymph nodes. |
Synchronous |
|
Ambelil M et al 20168 |
76/F |
Mandibular mass |
Past h/o PTC |
|
Kim H et al 20173 |
61/F |
Lungs with pleura |
19yrs |
|
Lee W 20179 |
72/M |
Lung, liver, bone & adrenal |
3 yrs |
|
Skwierslky S al 202021 |
77/F |
Cervical node, lungs |
5mths |
Table 2
Anaplastic transformation of thyroid carcinoma in cervical lymph node and/soft tissue neck.
|
Author/yr. |
Age/sex |
Duration & site |
Post op RT |
Follow-up |
|
|
Sato.K, et al 2006 22 |
77/M 62/M 80/M |
Cervical lymph node with rhabdoid phenotype. recur -mediastinal node 3 yrs simultaneous |
Not taken Not taken refused |
Died 6 mths Postop. Died of disease Alive |
|
|
Wiseman SM et al 2007 15 |
79/F |
Simultaneous |
Neck nodes and pharyngeal nodes |
|
|
|
Sung TY et al 2008 19 |
63/M 27/M |
7yrs 8yrs |
Not taken Not taken |
Died 3mths Died 4 mths |
|
|
Ito Y et al 2008 16 |
77/F |
2 yrs-Cervical node |
Not taken |
|
|
|
Khairy G 2009 13 |
90/F |
10yrs.cervical node & soft tissue neck |
Not taken |
expired. 6 days post –op. |
|
|
Deutschmann M et al 2013 17 |
60/M |
Simultaneous-cervical lymph node |
Given |
Alive after 1 yr. |
|
|
Agnes B et al et al 2018 14 |
79/m |
Lateral lymph node |
Not taken |
|
|
|
Cinamon U et al 2020 |
68/M |
10 yrs-cervical node |
Untreated |
Alive |
|
|
Song S et al 2020 20 |
85/M 77/M 62/M |
Co-existent -cervical node Simultaneous- cervical node 3yrs |
Refused Not taken Not taken |
Died 2mnths Died of disease Died of disease |
|
|
Present case.2021 |
75/F |
Right cervical lymph node and soft tissue with metastatic ATC and occult PTC |
Not taken |
- |
|
Figure 1
a)- Microphotograph of biopsy of metastatic neck deposit depicting fibromuscular tissue with an infiltrative tumor (H&E* x100); b)- The tumor is composed of polygonal cells with pleomorphic nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm showing squamoid features (H&E* x 400)
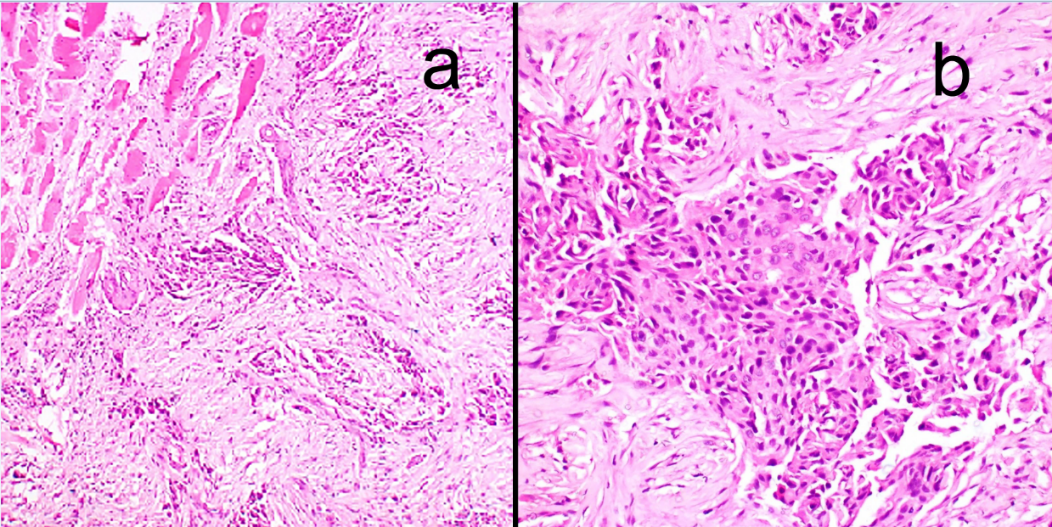
Figure 2
IHC images showing tumor cells expressing; a) CK and c) CK7; b) The tumor cells were negative for CK20; d) The tumor cells showing strong nuclear expression of p63. (A,B,C x100 and D x400)
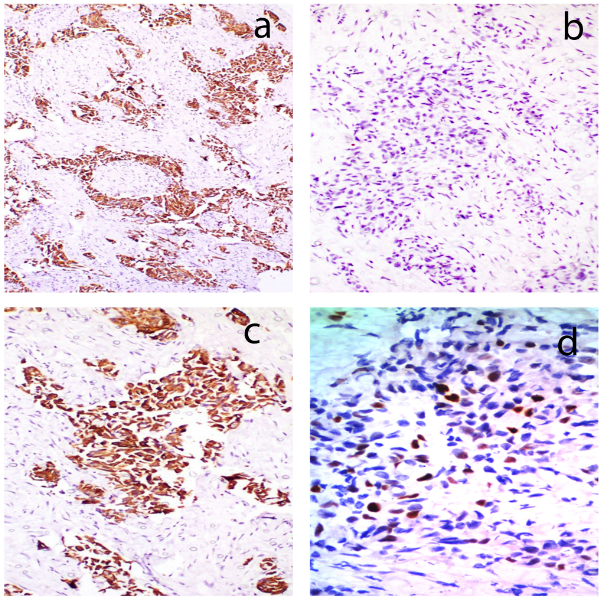
Figure 3
IHC images showing strong nuclear expression of; a) TTF1 and c) PAX8; b) The tumor cells were negative for GCDFP & d) CA125. (a,b,c and d x100)
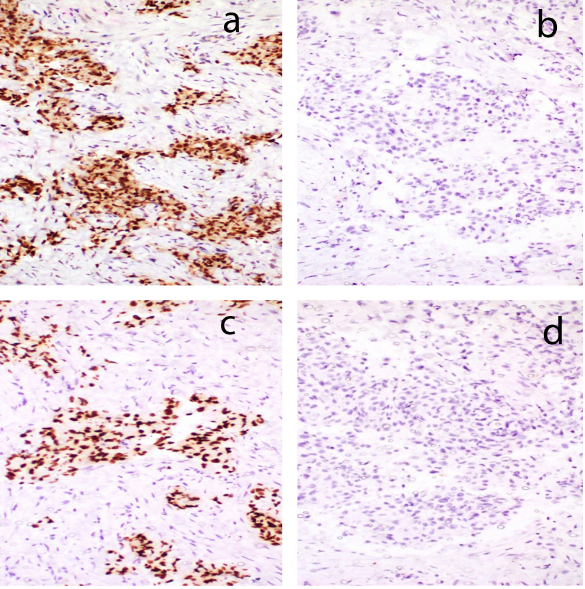
Figure 4
Gross photograph to show thyroidectomy specimen revealing brown gelatinous multinodular goitre with grey white nodules. Cut section of lymph node mass shows grey white tumor

Figure 5
a) Microphotograph showing foci of PTC within multinodular goitre (H&E* x100); b) high magnification shows papillary architecture with cells showing orphan Annie nuclei (H&E* x 400)
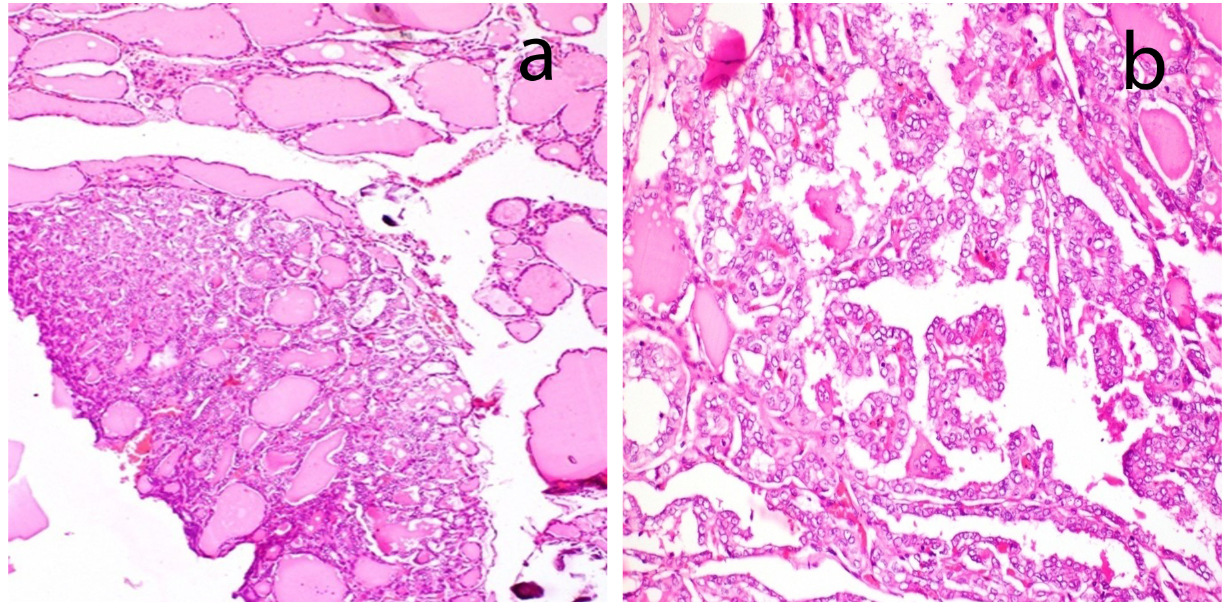
Figure 6
a): Microscopic picture of neck deposit showing sheets of spindle cells withsarcomatoid morphology (H&E*x 100); b): polygonal cells with nuclear pleomorphism and cytoplasmic clearing (H&E* x100); c): high magnification view to highlight numerous mitoses (black arrows) (H&E* x400); d): high magnification view of areas showing anaplastic cellswith pleomorphic, multinucleated bizarregiant cells (H&E* x 400); e): Microphotograph showing transition fromcarcinomatous area with nuclear clearing (in the upper part) to sarcomatoidarea (in the lower part) (H&E* x 100); f): sarcomatoid area withvascular tumor emboli (H&E *x 100).
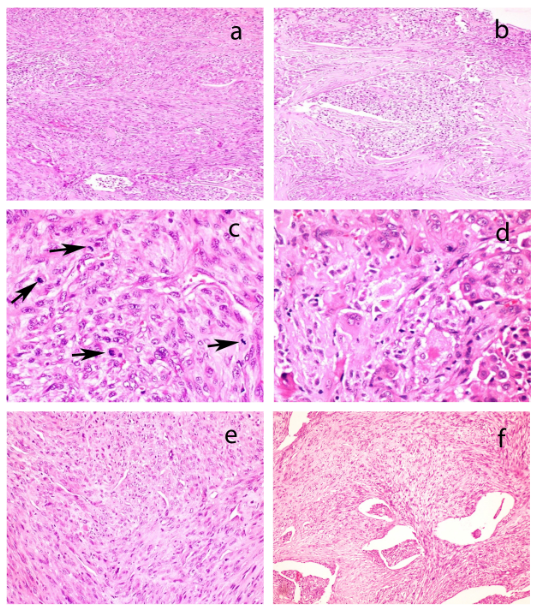
Figure 7
a) Scanner view of lymph node showing metastatic papillary carcinoma with psammoma body (arrows) and squamoid areas (arrow head) (H&E* x 40); b) Low magnification view to show papillary tumor with psammoma bodies (arrow) and squamoid morphology (arrowhead)(H&E* x 100); c) High magnification to highlight orphan Annie nuclei of PTC (H&E* x 400); d) High magnification to highlight squamoid morphology (H&E * x 400) *Hematoxylin and eosin

Discussion
Although anaplastic transformation (AT) of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is a known event in thyroid, this transformation is rare at metastatic site either in regional lymph node or at a distant site. On extensive literature search, we found total 30 cases of AT of thyroid carcinoma at metastatic sites. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 Majority of the case-reports had metachronous development of AT of treated or untreated PTC. This period varied from a year to as long as 25 years.2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 Distant metastasis can occur rarely in lung, brain, maxilla, bone and retroperitoneum. 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 Sixteen out of thirty cases showed distant metastasis as depicted in Table 1. Solomon et al., reported a case of distant metastasis where retroperitoneal metastasis showed AT, 25 years after thyroidectomy. Fifteen years after operative intervention he had metastatic PTC in cervical node and axilla. Hence, he underwent a second round of radioactive iodine but six years later presented with AT of retroperitoneal mass. He eventually died 3wks after surgery.2 Kim et al in 2017 reported an old Korean lady who had a near total thyroidectomy for PTC 19 years ago and presented with metastatic PTC in lungs and AT in pleura.3 Sotome et al reported a case where AT was seen in retroperitoneal region 17 years after the diagnosis of PTC on thyroidectomy. 4 Al Qsous W and Miller ID reported a case with multiple metastatic lung deposits ten years after treatment.5 Four out of five cases reported by Ito et al showed AT in metastatic foci of lungs, axilla and submandibular areas years after primary PTC.6 Similarly cases described by Takeshita et al, Ambilil et al, Lee W and Kim D, Nakayama et al, Abe et al, Kaushal et al showed metastasis at varied interval to different sites as cited in Table 1. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
Fourteen cases of AT of thyroid carcinoma were found in cervical lymph node and soft tissue (Table 2). Case reported by Khairy G was an elderly lady who had an untreated huge thyroid mass since past 10 years; was operated and found to have PTC with AT in cervical nodes. 13 She did not survive and died immediately on 10th postoperative day. Agnes et al, Wiseman et al, Cinamon et al and one out of five cases reported by Ito et al had AT in the metastatic cervical node.6, 14, 15, 16 Deutschmann et al., in 2013 reported a case of an old lady who had a thyroid mass and enlarged supraclavicular lymph node. FNAC of the cervical lymph node mass showed PTC, she underwent thyroidectomy with excision of the supraclavicular nodal mass. Thyroidectomy revealed multiple papillary microcarcinomas and supraclavicular mass showed metastatic PTC with AT. In our case, the old lady presented with neck metastasis showing anaplastic features and later the search for primary disclosed multiple foci of occult PTC.17
The frequency of synchronous occurrence of AC and PTC is relatively less. Benedict M & Costa J reported a case who succumbed with metastatic PTC and coexistent AT in multiple sites including bilateral lungs, aorta, pericardium, adrenal, mediastinal, and hilar as well as abdominal lymph nodes.18 A case reported by Song et al in 2020 had coexistent PTC & AT in cervical node who developed lung metastasis after 5 months.20 Similarly cases reported by S Wiseman et al and one of the cases of Sato K et al had concurrent PTC and AT in cervical node.15, 22 Our case is unique in the sense, it presented with AT in the metastatic deposit which posed a diagnostic challenge and the PTC in the thyroid was detected subsequently in the thyroidectomy specimen.
AC is a disease of old age although very rarely it can affect young age. Age range varied between 27-80 years. Most of the patients complain of rapidly enlarging neck mass and pressure related symptoms like dysphagia, pain, hoarseness of voice or dyspnea.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 In our case, the elderly lady presented with progressively enlarging lateral neck mass which resulted with pressure related symptoms.
Time interval between primary diagnosis of PTC to its AT ranged from months to as long as 30 years. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22 There is still dispute to be settled about the relationship between post-operative radioactive iodine and AT.
Morphology remains the cornerstone for diagnosis. However, equivocal morphology poses a great challenge in metastatic deposits. We encountered greater difficulty in our case on needle biopsy because we were dealing with metastatic deposits of unknown primary, where neoplastic cells had squamoid features with clear cytoplasm which initially led us to suspicion of metastatic poorly differentiated carcinoma. Upper aero-digestive tract (UADT), salivary gland, thyroid, breast, rarely stomach, lung, as well as Melanoma of UADT make the list of differential diagnosis as a likely primary in metastatic neck deposit. In view of the squamoid morphology, our primary panel consisted of CK7, CK20 and p63. However, due to co-expression of CK7 and p63, we were forced to think of other possibilities and hence we designed our secondary panel accordingly. Expression of PAX8 and TTF1 suggested primary in thyroid. However, expression of p63 still needed to be explained. In thyroid, p63 expression is usually seen in PTC, poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC) and AC. However, even after careful search, we could not demonstrate nuclear features of PTC on initial needle biopsy of neck mass. Hence we favored the possibility of AC or PDTC possibly on the background of PTC and advised thyroidectomy which showed multifocal PTC in thyroid with AT in metastatic neck deposit.
IHC serves a useful tool in addition to morphology in such challenging cases. Presence of differentiated thyroid carcinoma or thyroid specific markers like thyroglobulin and TTF-1 help diagnose the anaplastic component of differentiated thyroid malignancy.23 At times anaplastic transformation at metastatic sites denies IHC differentiation as well; which makes situation worse for diagnosis. The marker p63 is thought to be useful in diagnosis of PTC by its high specificity (99.2%) and positive predictive value (95%). PAX 8 has a diagnostic utility role as immunoreactivity is 79% in PTC.23
Multifocal mutational aggregation leads to multicentricity and is a well-known feature of PTC. Advanced molecular technologies have provided an insight to the stepwise pathogenesis of PTC.23, 24 The multistep process of genetic and epigenetic changes involves a progressive accumulation of genetic mutations of BRAF (30%), RAS (60%) and TERT promoter. This increasing mutational burden along with down regulation of Bcl2 culminates into transformation of differentiated thyroid carcinoma to its de-differentiated form.24 Some mutations can predict high risk for AT in PTC cases like E cadherin/catenin, TP53 or TERT hence, hold a promising role.24
Treatment protocol for PTC with transformation to AC includes total thyroidectomy with ipsilateral radical neck dissection (RND) plus radiotherapy (RT).25 With distant metastases the regimen is radiation with or without surgical exploration along with chemotherapy. Anaplastic carcinoma (AC) carries a dismal prognosis with mortality more than 90%. Death usually occurs within a year of diagnosis as was seen in numerous cases. Median survival ranges from 4 to 12 months. Five year survival rate is less than 10%. Poor prognostic factors include old age at diagnosis, male gender, leukocytosis, large tumor size, extrathyoidal extension and distant metastasis.25
Conclusion
Transformation of well differentiated thyroid carcinoma to less differentiated anaplastic carcinoma, although a known phenomenon, poses a diagnostic challenge at metastatic site, especially so, when primary site is small/hidden or shows no such transformation. This rapid downhill progression jolts the prognosis from good to bad. Hence, one should be skeptical and bear a high index of suspicion while dealing with metastatic neck mass showing anaplastic morphology. Utility of IHC in subtle cases is promising and aids in precise diagnosis. Some mutations can predict high risk for AT in PTC cases like E cadherin/catenin, TP53 or TERT hence, genetic profiling carries promising results.
