- Visibility 186 Views
- Downloads 10 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.jdpo.2020.053
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Comparison of automated method and photometric cyanmethemoglobin method for haemoglobin estimation
- Author Details:
-
Dileep Kumar Jain *
Introduction
Hemoglobin comprises of four globin protein subunits, each having one polypeptide chain and one heme group. Oxygen binds reversibly to the ferrous iron atom in each heme group.[1], [2] Main function of haemoglobin is to transport oxygen from lungs to the tissues, where oxygen is utilized for metabolism,[3] mainly to facilitate oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria.[4] Anaemia is very common in our country, worldwide it affects over 800 million women and children, [5] also there are fair number of cases in advanced countries like US, [6] so haemoglobin is advised frequently to the patients especially in antenatal patients because of increased risk of complications.[7] Hb measurement is also essential for screening the eligibility of donors in blood banks.[8] The reference range for normal hemoglobin (according to WHO) is 13-18 gm/dl for men, 12-16 gm/dl for women. [9], [10]
Hemoglobin being one of the commonest investigations in laboratory, we require economical, feasible and accurate method. [11] Many methods are commonly used, sahli’s acid hematin method, cyanmethemoglobin method by photometer, automated method by cell counters. [3] Different lab uses different methods depending on laboratory location, number of patients, availability of technical staff, problem of electricity, affordability. There is variation in hemoglobin measurement done by different instruments due to many reasons including type of sample. [10]
Photometric cyanmethemoglobin method is based on principle that Drabkin reagent reacts with hemoglobin in blood to form cyanmethemoglobin and developed colour is measured by photometry at 550 nm. Automated method on Mindray cell counter is based on principle of electrical impedance for cell counting and colorimetry for HB estimation.[12] Automated method uses a non cyanide hemoglobin method. [13]
Aims and objective
The study were to evaluate accuracy, cost effectiveness, suitability and feasibility of photometric versus automated method of haemoglobin estimation.
Materials and Methods
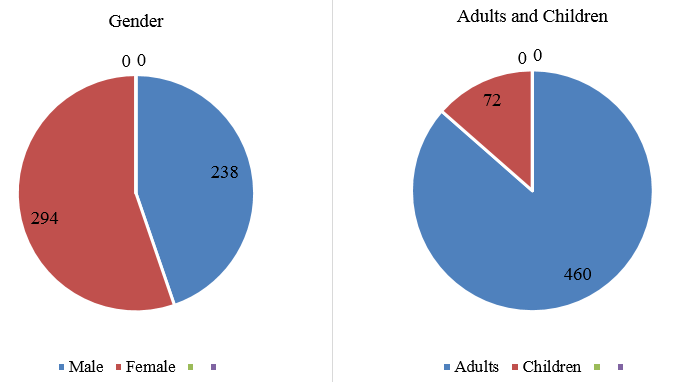
We took 532 patient’s (460 adults and 72 children) Hb estimation into consideration between May 2019 to Aug 2019 including indoor & outdoor patients attending Hind Institute of Medical Sciences, Safedabad, Barabanki, Uttar Pradesh. Adults were between 15 to 85yrs of age. Children were less than 15yrs upto 03 hrs old, newly born baby. 2 ml blood samples were collected in tubes containing K3EDTA anticoagulant. After proper mixing on blood shaker Hb estimation was done simultaneously both by Mindray 5 part hematology cell counter (BC-5150) and digital colorimeter by Aimil. For manual method 5 ml Drabkin’s reagent was taken in test tube and 20 ul of blood was mixed and then waited for 5minutes at room temperature before taking absorbance on colorimeter at 550 nm filter against Drabkin,s solution. A standard curve is used to know the Hb concentration in the sample by measuring absorbance compared to standard control. Drabkin’s solution contains cyanide which is hazardous during handling and disposal. [5] Drabkin’s reagent was used from Arkray (formerly Span Diagnostics). Standards were also used from same company. For automated cell counter, control blood was used from Diagon. Standards (control) were run regularly. We did not include hemolyzed sample in our study.
Results
A total of 532 samples were processed for hemoglobin estimation. Out of these 238 were males and 294 females, 460 adults, 72 children. Mean haemoglobin concentration on Mindray cell counter for adults and children were 10.62±2.26 and 10.12±2.41 respectively. Mean haemoglobin concentration by cyanmethemoglobin method on photometer (AIMIL) for adults and children were 10.84±2.05 and 10.42±2.32 respectively. This shows mean by photometric method is greater by 2.07% for adults and 2.96% for children. Accuracy of both the methods was compared using Microsoft Excel software.
This showed 2.52 % (overall) increase in results by manual method. Comparison of different parameters is tabled.
| Variable | Mindray Cell Counter (BC-5150) | Aimil Digital Photometer |
| Number of patients | 532 | 532 |
| Mean Hb of Adults | 10.62 | 10.84 |
| Mean Hb of Children | 10.12 | 10.42 |
| Lowest Hb among Adults | 3.40 | 4.10 |
| Highest Hb among Adults | 16.80 | 15.10 |
| Lowest Hb among Children | 4 | 4.5 |
| Highest Hb among Children | 18.9 | 19.1 |
| SD (Adults) | 2.26 | 2.05 |
| SD(Children) | 2.41 | 2.32 |
| Costof instrument | Rs 400,000 | Rs 9,500 |
| Coefficient of Variation of Controls | 2.2% | 2.9% |
| Reagent Stability | Stable | Stable |
| Technical Skill | Not required | Required |
It takes 5 minutes by automated method while 15-20 minutes by photometric method. Photometer requires almost negligible maintenance while automated analyser regular maintenance.




Discussion
For a developing country like India, economically suitable methodology is the need of the hour. At our institute cost of the test by automated cell counter is Rs 100 whereas cost of manual photometric method is Rs 10 per test. Cost of Mindray Cell Counter is about Rs 4.0 lakh while AIMIL photometer cost only for Rs 9,500. When haemoglobin is the only test required, photometric method is cost effective and feasible. Automated method should be used where complete blood count (CBC), or multiple parameters are required. [14] International committee for standardization in haematology (ICSH) has recommended the‘Drabkin’ as the method of choice and have suggested all the other method should be adjusted to be comparable to this method [15] because of availability of internationally accepted reference standard calibrator. [16], [17] Periodic standards (controls) must be run to maintain accuracy both in manual & automated method. Hemoglobin estimation by automated cell counters is the next best method.[18] There is a significant and positive correlation between the manual and the automated method.[19] For accuracy proper sample collection and proper technique is very important.[20]
Conclusion
Both methods of Hb estimation are accurate and for single parameter manual method is very cost effective.
Abbreviations
Hb: Hemoglobin
HIMS: Hind Institute of Medical Sciences
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Marengo-Roweaj. Structure-function relations of human hemoglobins. Inbaylor Univ Med Center Proc 20061. [Google Scholar]
- J A Lukin, C Ho. The structure− function relationship of hemoglobin in solution at atomic resolution. Chem Rev 200410. [Google Scholar]
- Azim Waqar, Parveen Shahida, Parveen Saadat. Comparison of photometric cyanmethemoglobin and automated methods for hemoglobinestimation. National Centre Biotechnol Inf 2002. [Google Scholar]
- C Thomas, Lumbab. Physiology of haemoglobin. Continuing Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 201231. [Google Scholar]
- Crystal D. Karakochuk, Sonja Y. Hess, Denish Moorthy, Sorrel Namaste, Megan E. Parker, Aviva I. Rappaport, . Measurement and interpretation of hemoglobin concentration in clinical and field settings: a narrative review. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chh Le. The Prevalence of Anemia and Moderate-Severe Anemia in the US Population (NHANES 2003-2012). PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar]
- S Swaminathan, T Thomas, Kurpadav Boseb. Point of care haemoglobin estimation. Indian J Comm Health 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ralph D Whithead, Zuguo Mei, Carine Mapango, Maria Elena D. Jefferds. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Waalen Beutlere. The denition of anemia: what is the lower limit of normal of the blood hemoglobin concentration. Blood 20061. [Google Scholar]
- C P Price, I Smith, Van den Bruel. Improving the quality of point-of-care testing.. Family Pract 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sankhesv Anchinmanevt. Evaluation of hemoglobin estimation with non-cyanide alkaline haematin d-575 method. Int J Res Med Sci 201619. [Google Scholar]
- John P. Greer. Wintrobe, wintrobe's clinical hematology. . [Google Scholar]
- M Toppo, D K Pal, D Gour, V Melwani, M Dubey, A Mishra. Comparison of Performance of Digital Hemoglobinometer over Automated Hematology Analyzer for Hemoglobin Estimation and Its user-friendliness among the Pregnant Women in Selected District Hospitals of Madhya Pradesh. Indian J Community Med 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wasnik Madhura, Wasnik Nitin, Tirpude Rakhi, Vijay P Agrawal. Validation of different tests for haemoglobin estimation. . Int J Biomed Adv Res 2014. [Google Scholar]
- P Balasubramaniam, A Malathi. Nicotine mediated activation of Pak1/NFkB cascade in pancreatic cancer cells – A pilot study. Eur J Mol Clin Med 1992. [Google Scholar]
- T Srivastava, H Negandhi, S B Neogi, J Sharma, R Saxena. Methods for Hemoglobin Estimation: A Review of “What Works. J Hematol Transfus 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bshah Vinaya, G VPuranik, S Shah Bipin. Evaluation of non cyanide methods for hemoglobin estimation. Indian J Pathol Microb 2011. [Google Scholar]
- N. Shah, E. A. Osea, G. J. Martinez. Accuracy of noninvasive hemoglobin and invasive point-of-care hemoglobin testing compared with a laboratory analyzer. Int J Labor Hematol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- AliyuA Babadoko, IsmailaN Ibrahim, AbubakarU Musa, Nasiru Usman. Reproducibility of hematological parameters: Manual versus automated method. Sub-Saharan Afr J Med 2016. [Google Scholar]
- S Burger, J Pierre-Louis. A procedure to estimate the accuracy and reliability of hemocue™ measurements of survey workers. Washington: ilsi. 2003. [Google Scholar]
